3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing or layer-by-layer manufacturing, is a technology that constructs objects by laying self-bonding materials such as powdery metal, thermoplastic filament or resin according to digital 3D model files. The first commercial 3D printer was released by an American company in the mid-1980s.
It builds up a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. In the process, the feeding material is deposited, joined or solidified continuously layer by layer. And every layer of them can be regarded as one thin cross-section of the printed model.
Also, 3D printing is an additive process. It is different from subtractive manufacturing, where a lathe or milling machine removes/hollows out some unwanted parts from a larger and integral piece of raw material in order to get an object in the desired shape. That is to say, 3D printing can create objects in complex shapes by consuming less material. For further details, let’s take a look at how 3D printers work!
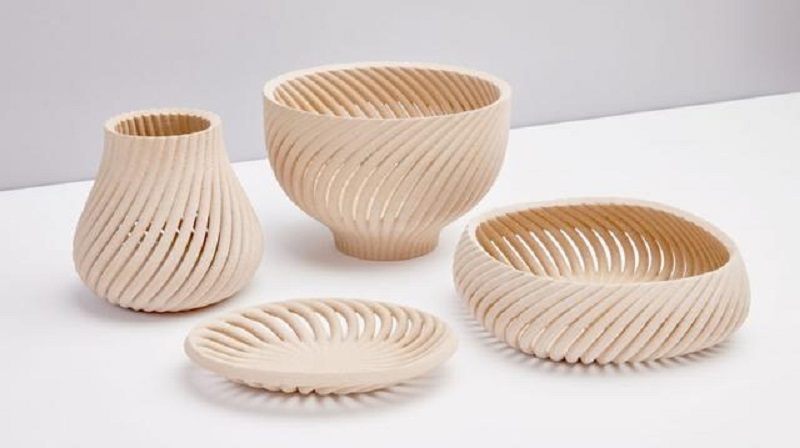

Three steps of 3D printing
Generally speaking, three steps are required to use the 3D printer to print an object.
1. Get 3D Model Files
3D printing begins with a 3D model. You can create a 3D model file from scratch or download from the online website of the 3D library.
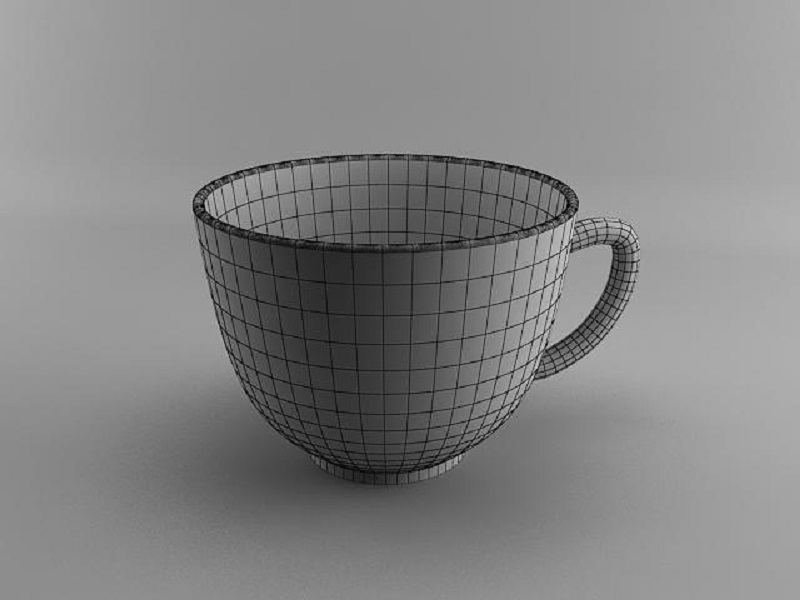

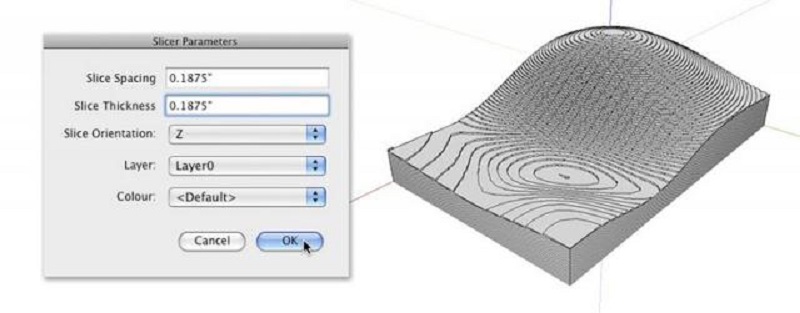
2. 3D Model Slicing
There is various 3D model slicing software we can choose to use, from industry grade to open source. If you have finished your model design, the following step is to slice your digital file for printing preparation. To do this, you need to slice your 3D model into hundreds or thousands of layers with slicing software.
3. Bring Printable Files to 3D Printers for Printing
Once you have sliced your model file, you can print it. Just transfer your files to the 3D printer via USB disk, SD card, or WiFi. Then, the model can be printed layer by layer.
Development of the 3D Printing Industry
Early on, 3D printing was only suitable for prototyping and one-off manufacturing. But it has been improving rapidly in print quality, precision, speed and stability. Today, it is considered viable as an efficient industrial-production technology.
According to Acumen Research and Consulting, the global 3D printing market is estimated to reach $41 billion in 2026. Though most of the demands for 3D printing are industrial, 3D printing is going to change every major industry and how we live, work and play in the future with its rapid development.
Application in Rapid Prototyping & Rapid Manufacturing
Since the late 1970s, a number of businesses have been using 3D printers to create design prototypes. So, 3D printing came into prominence as a way to quickly build prototypes.
Why do we need 3D printers to do rapid prototyping?
In short, it is fast and relatively economical. As it takes a few days to get the prototypes, instead of several weeks. You also don’t need costly molds or tools, so it is cheaper and easier to iterate.
Besides the rapid prototyping for building models, 3D printing can also be done for rapid manufacturing. It is a burgeoning way for companies to do short-term and small batch custom manufacturing.